The International Space Station (Zarya) is the largest satellite ever constructed and easily visible from earth. It is maintained in orbit between 278 Km and 470 Km altitude. And travels at an average ground speed of 27,72 kmph, completing 15.7 orbits per day.
It is habitable and serves as a Research Laboratory that has a microgravity environment. Crews inside conduct experiment in many fields including biology, human biology, physics, astronomy and meteorology.
Steps to see the ISS from Earth without any telescope
Step 1: Head on to the location page of HeavensAbove.com
Step 2: Select your location either by typing your city in the search bar or from the map, then scroll down and click “Update” (Refer the animated GIF below)
Step 3: Now under the Satellites section click “ISS“, you will get a table that displays 10 days prediction of when you can see the International Space Station in your location. Click on any date to see a chart representing the ISS path.
The more the negative value in the second column, the more the brightness will be, for example
-3.3 = ISS will be brighter
-0.2 = ISS will be less visible

Why can’t you see ISS during day or night
The Space Station is visible just because it reflects the Sun’s light, During day the sunlight is much brighter and dominates the reflected light and during Night there is no Sunlight for reflection or glow of ISS. So, it is only visible during Sunrise and Sunset, also the Geographic Position and path of its motion plays an important role in the visibility.
Current Live Position of the International Space Station
Where is the International Space Station right now? If you are curious about the current location of the International Space Station, check out the following websites, Heavens-Above.com, N2YO, Astroviewer and ISS Tracker
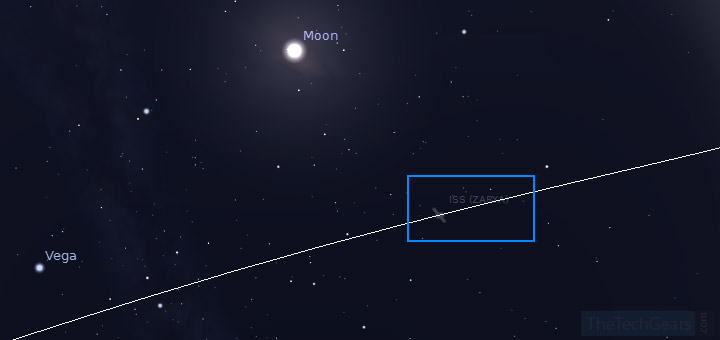
Simulating ISS Path using Planetarium Software
You can also use a Planetarium Software like “Stellarium”, and simulate the path of International Space Station. Stellarium is availabe for Windows, Mac and Linux.
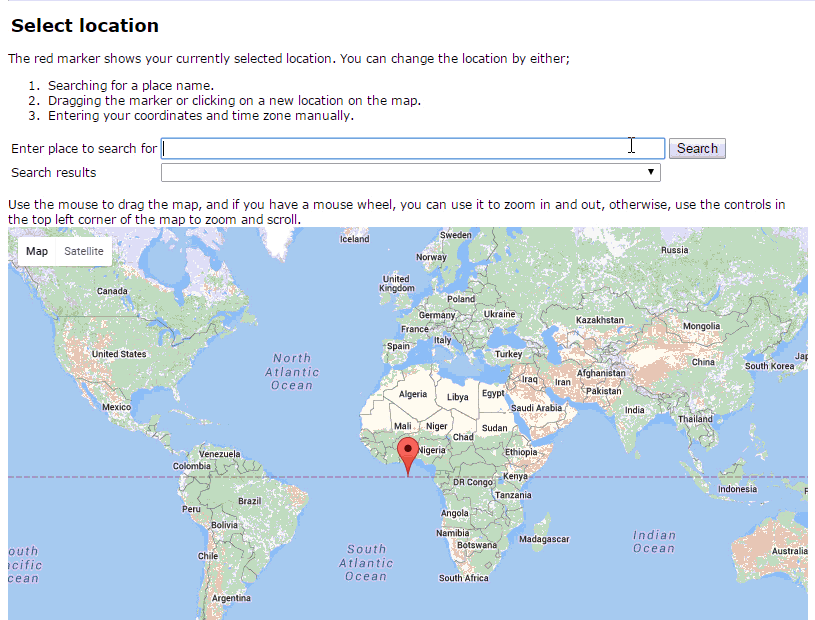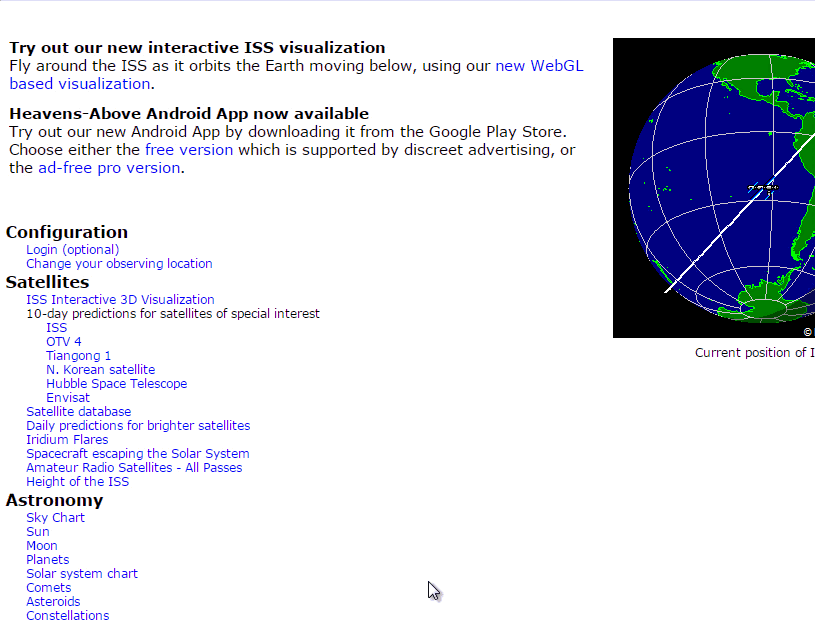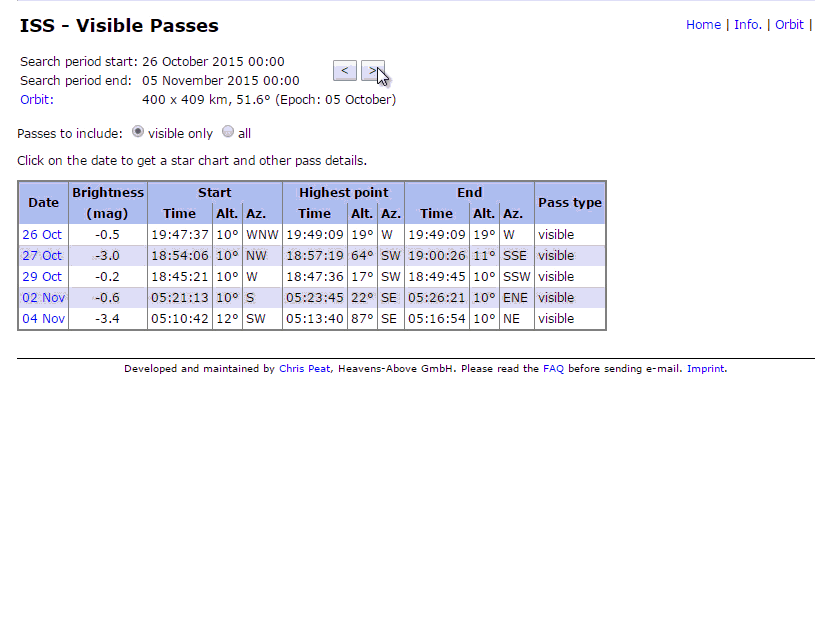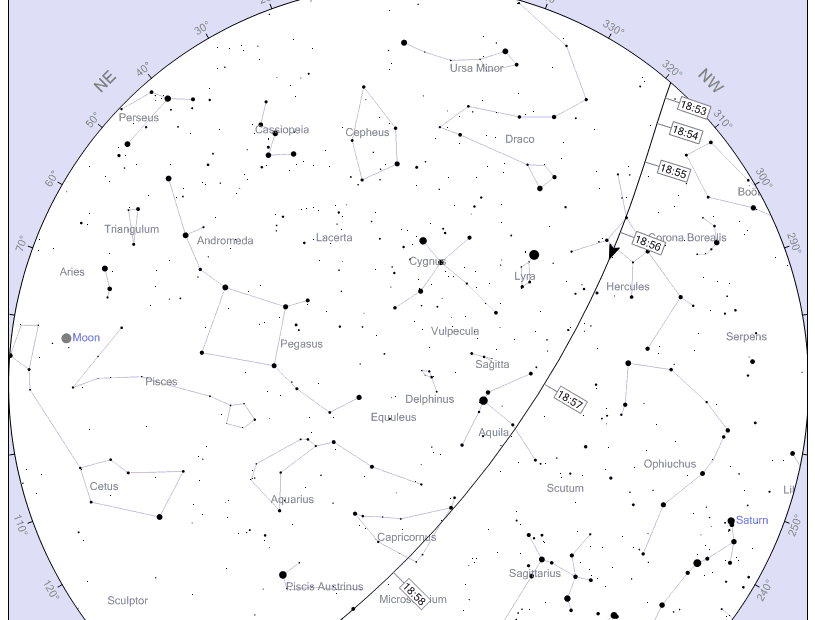
Understanding the Visible Passes Table
1. Date
2. Mag:
This indicates “Magnitude” Higher (-)Negative magnitude values indicates more brightness, for example, a magnitude value of –3.6 is more brighter and 0.4 is less brighter and less visible. Click here for more information on “Magnitude”
3. Starts:
Time: This is the time when ISS rises and becomes visible
Alt.: Altitude indicates the angle at which ISS becomes visible, usually this value is 10 while ISS starts appearing.
Az.: Azimuth may have somewhat astronomically complex definition, but for now, just take it as the direction in which the ISS appears.
4. Max:
Time: This is the time when ISS becomes visible at its peak level
Alt.: Here altitude indicates the angle at which ISS is at its peak, It is more brighter and more visible when Max Altitude is higher like 77, higher value indicates that the Space Station would pass through the centre of the sky
Az.: The direction or orientation in which the ISS is at its peak visible point to the observer
5. Ends:
Time: This is the time when ISS Disappears
Alt.: Here altitude indicates the angle at which ISS disappearsAz.: The direction in which ISS sets down and disappears
[This article was first published on April 08, 2012 and was updated on October 06, 2015]








![15+ Best and Must-Have Software for your New PC [2020] 15-Best-and-Must-Have-Software-for-your-New-PC-2020-Edtion](https://thetechgears.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/15-Best-and-Must-Have-Software-for-your-New-PC-2020-Edtion-324x160.jpg)
![15+ Best and Must-Have Software for your New PC [2020] 15-Best-and-Must-Have-Software-for-your-New-PC-2020-Edtion](https://thetechgears.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/15-Best-and-Must-Have-Software-for-your-New-PC-2020-Edtion-100x70.jpg)


Its good and interesting.Nice article.